이 글은 코틀린 언어 문법을 빠르게 훑으며 학습한 내용을 바탕으로 작성한 글입니다.
Kotlin 공식 Document를 보시면 훨씬 더 깊은 이해를 하실 수 있습니다. 이 글은 제가 보고 제 마음대로 정리한 글입니다.
이름하여 빠뽀. 코틀린 기본 문법 빠르게 뽀개기. 스따또.
Kotlin Docs | Kotlin
kotlinlang.org
1. 데이터 타입
Basic types | Kotlin
kotlinlang.org
1. Integer types
| Type | Size(bits) | Min value | Max value |
Byte |
8 | -128 | 127 |
Short |
16 | -32768 | 32767 |
Int |
32 | -2,147,483,648 (-$2^{31}$) | 2,147,483,647 ($2^{31} - 1$) |
Long |
64 | $-2^{63}$ | $2^{63} - 1$ |
UByte |
8 | 0 | 255 |
UShort |
16 | 0 | 65535 ($2^{16} - 1$) |
UInt |
32 | 0 | $2^{32} - 1$ |
ULong |
64 | 0 | $2^{64} - 1$ |
2. Floating-point types
| Type | Size(bits) | Significant bits | Exponent bits | Decimal digits |
Float |
32 | 24 | 8 | 6-7 |
Double |
64 | 53 | 11 | 15-16 |
3. Boolean : true and false
4. Char
5. String: sequence of characters in double quotes(")
*String templates: $기호를 앞에 붙이거나 $와 curly braces로 감싸면 해당하는 코드가 계산되어 string에 결합됩니다.
val i = 10
println("i = $i") // Prints "i = 10"val s = "abc"
println("s.length is ${s.length}") // Prints "abc.length is 3"
2. 변수와 상수 (Variable and Constant)
- 변수는
var키워드를 사용하여 선언하고 값을 할당할 수 있습니다. 변수 선언만 할 때에는 타입을 꼭 명시해주어야 하지만, 선언 후 바로 초기화를 할 때에는 할당된 값을 바탕으로 코틀린이 자료형을 추론해줍니다.
val a: Int = 1 // immediate assignment
var b: Int // Type required when no initializer is provides
var c = 3 // 'Int' type is inferred- 상수(Constant; Read-only local variable)는
val키워드를 이용해 정의합니다.
3. 조건문(Condition Expression)
1. if statement
- 비교 연산자:
==,!=,<,>,<=,>= - 논리 연산자:
ll(OR),&&(AND),!(NOT) - single condition:
if
exclusive condition:if ... else ...
branches:if ... else if ... else ...
// Single condition
var max = a
if (a < b) max = b
// Exclusive condition
var max: Int
if (a > b) {
max = a
}
else {
max = b
}
// Branches
var max: Int
if (a > b) {
max = a
}
else if (a < b) {
max = b
}
else {
max = a
}
// As expression
val max = if (a > b) a else b
val max = if (a > b) {
print("Choose a")
a
} else {
print("Choose b")
b
}2. when statement
다른 프로그래밍 언어의 switch-case statement와 같은 문법입니다.
val grade = "A+"
when (grade) {
"A+" -> println("Excellent")
"A0" -> println("Good")
"B+" -> println("Not Bad")
"B0" -> println("Bad")
}
// with comma
val grade = "F"
when (grade) {
"A+", "A0", "B+", "B0" -> println("Good")
"C", "D", "F" -> println("Bad")
}
// in or !in syntax for a range check
val score = 90
when (score) {
in 90..100 -> println("A+")
else -> println("retake")
}
// without a parameter(replacement for an if statement)
val scroe = 49
when {
score > 90 -> println("A+")
score in 50..89 -> println("A0")
else -> println("retake")
}
// Type checking (is syntax)
val x: Any = 20.5
when (x) {
is Int -> println("Int")
is String -> println("String")
else -> println("I don't know")
}
// As expression
val score = 80
var grade = when (score) {
in 90..100 -> "A+"
else -> "F"
}
4. Array
Array()Constructor는 배열의 크기와 원소의 값을 반환하는 함수를 받습니다.arrayOf()는 원소의 값을 받습니다.- primitive type array:
ByteArray,ShortArray,IntArray,LongArray,CharArray,FloatArray,DoubleArray,BooleanArray
// using Array()
val arr1 = IntArray(5) // create IntArray with size of 5
val arr2 = IntArray(5) {42} // create IntArray with size of 5, values of 42
val arr3 = IntArray(5) {it + 1} // create IntArray with size of 5, values of index + 1
val arr4 = IntArray(5) {i -> i * i} // create IntArray with size of 5, values of index + 1
// using arrayOf()
val x = arrayOf("One", "Two", "Three")
val y: IntArray = IntArrayOf(1, 2, 3)get(),set(),first(),last(),sort(),sortedArray()등의 uility 함수들을 사용할 수 있으며java.util.Arrays의toString()함수를 가져다 사용할 수도 있습니다. (Kotlin은 java와 완벽호환됩니다.)
import java.util.Arrays
fun main() {
val arr: IntArray = IntArray(10) {it + 1}
val first = arr[0]
val first2 = arr.first()
val first3 = arr.get(0)
val last = arr.last()
arr.sort()
println("arr: ${Arrays.toString(arr)}") // Prints "arr: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]""
println("Size of arr: ${arr.size}") // Prints "Size of arr: 10"
arr[0] = 100
arr.set(1, 200)
val arr2 = arr.sortedArrayDescending()
println("arr2: ${Arrays.toString(arr2)}") // Prints "arr2: [200, 100, 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3]""
}
5. Collections
Collections overview | Kotlin
kotlinlang.org
Collections란 여러 개의 값들을 동적으로 저장하기 위한 공간입니다. 코틀린에서도 다른 언어들과 비슷하게 list, set, map 3가지 collection을 제공합니다. 각각의 collection들은 immutable collection과 mutable collection으로 나눌 수 있습니다.
- immutable collection: collection 원소에 접근하여 읽는 인터페이스만 제공합니다. 즉, 한 번 값이 부여되면 수정할 수 없습니다. (Read-only)
- mutable collection: 원소를 추가하고 삭제하고 값을 변경하는 것이 가능합니다.
1. List
인덱스로 원소에 접근할 수 있는 순서를 가지는 collection입니다. 순서를 가지므로 중복이 허용됩니다.
fun main() {
val numbers = listOf("one", "two", "three", "four")
println("Number of elements: ${numbers.size}") // Prints "Number of elements: 4"
println("Third element: ${numbers.get(2)}") // Prints "Third element: three"
println("Fourth element: ${numbers[3]}") // Prints "Fourth element: four"
println("Index of element \"two\" ${numbers.indexOf("two")}") // Prints "Index of element "two" 1"
}- LIst-specific write operations:
add(),removeAt(),shuffle(), Indexing([])
fun main() {
val numbers = mutableListOf(1, 2, 3, 4)
numbers.add(5)
numbers.removeAt(1)
numbers[0] = 0
numbers.shuffle()
println(numbers) // Prints "[4, 5, 0, 3]""
}
2. Set
중복 없이 unique한 원소들의 집합입니다. 순서를 가지지 않습니다.
fun main() {
val numbers = setOf(1, 2, 3, 4)
println("Number of elements: ${numbers.size}") // Prints "Number of elements: 4"
if (numbers.contains(1)) println("1 is in the set") // Prints "1 is in the set"
val numbersBackwards = setOf(4, 3, 2, 1)
println("The sets are equal: ${numbers == numbersBackwards}") // Prints "The sets are equal: true"
}- Set-specific write operations:
add(),remove()
fun main() {
val numbers = setOf(1, 2, 3, 4)
val numbersBackwards = setOf(4, 3, 2, 1)
numbers.add(5)
numbersBackwards.add(5)
numbers.remove(4)
numbersBackwards.remove(4)
println("numbers: ${numbers}") // Prints "numbers: [1, 2, 3, 5]"
println("numbersBackwards: ${numbersBackwards}") // Prints "numbersBackwards: [3, 2, 1, 5]"
}
3. Map
: key-value 쌍의 집합입니다. 키는 unique하며, 하나의 키는 하나의 value에 map됩니다.
fun main() {
val numbersMap = mapOf("key1" to 1, "key2" to 2, "key3" to 3, "key4" to 1)
println("All keys: ${numbersMap.keys}") // Prints "All keys: [key1, key2, key3, key4]"
println("All values: ${numbersMap.values}") // Prints "All values: [1, 2, 3, 1]"
if ("key2" in numbersMap) println("Value by key \"key2\": ${numbersMap["key2"]}") // Prints "Value by key "key2": 2"
if (1 in numbersMap.values) println("The value 1 is in the map") // Prints "The value 1 is in the map"
if (numbersMap.containsValue(1)) println("The value 1 is in the map") // same as previous (Prints "The value 1 is in the map")
}- Map-specific write operations:
put(),remove()
fun main() {
val numbersMap = mutableMapOf("one" to 1, "two" to 2)
numbersMap.put("three", 3)
numbersMap["one"] = 11
println(numbersMap) // Prints "{one=11, two=2, three=3}"
}
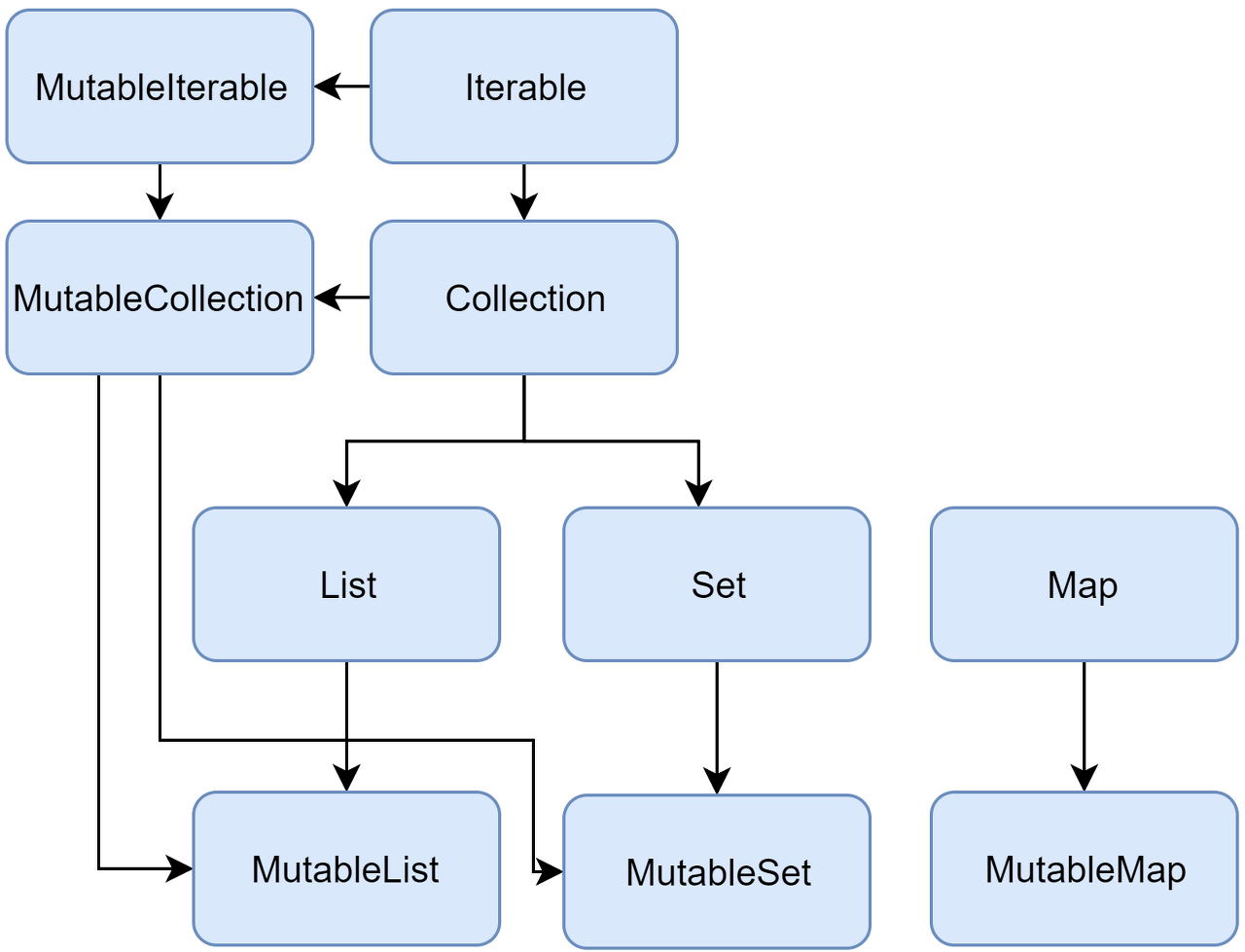
4. Functions for Collections
map(): 주어진 lambda function을 각각의 collection 원소에 적용시켜 새로운 리스트를 반환해주는 함수 (결과로 반환된 리스트 원소들의 순서는 원래 원소들의 순서와 동일)
val numbers = setOf(1, 2, 3)
println(numbers.map { it * 3 }) // Prints "[3, 6, 9]"
println(numbers.mapIndexed { idx, value -> value * idx }) // Prints "[0, 2, 6]"val studentGrade = mutableMapOf<String, Int>()
studentGrade.put("Student1", 100)
studentGrade.put("Student2", 90)
studentGrade.put("Student3", 80)
val name = studentGrade.mapKeys {it.key + "new"}
println(name) // Prints "{Student1new=100, Student2new=90, Student3new=80}"
val grade = studentGrade.mapValues {it.value / 10}
println(grade) // Prints "{Student1=10, Student2=9, Student3=8}"zip(): 두 개의 collection에서 동일한 위치에 있는 원소들의 쌍을 만들어 주는 함수
val colors = listOf("red", "brown", "grey")
val animals = listOf("fox", "bear", "wolf")
println(colors zip animals) // Prints "[(red, fox), (brown, bear), (grey, wolf)]"
val twoAnimals = listOf("fox", "bear")
println(colors.zip(twoAnimals)) // Prints "[(red, fox), (brown, bear)]"
println("${colors.zip(animals) { color, animal -> "The ${color.replaceFirstChar { it.uppercase() }} is $animal" }}")
// Prints "[The Red is fox, The Brown is bear, The Grey is wolf]"filter()first()/last()minOrNull()/maxOrNull()average()sum()count()iterator()
6. Loop
1. for
fun main() {
for (i in 1..3) {
println("hellomygreenworld")
}
/* Prints
"hellomygreenworld
hellomygreenworld
hellomygreenworld"
*/
for (i in 6 downTo 0) {
println("6DownTo0: $i")
}
/* Prints
"6DownTo0: 6
6DownTo0: 5
6DownTo0: 4
6DownTo0: 3
6DownTo0: 2
6DownTo0: 1
6DownTo0: 0"
*/
for (i in 1..11 step 3) {
println("1..11 step 3: $i")
}
/* Prints
"1..11 step 3: 1
1..11 step 3: 4
1..11 step 3: 7
1..11 step 3: 10"
*/
for (i in 1 until 11 step 2) {
println("1 until 11 step 2: $i")
}
/* Prints
"1 until 11 step 2: 1
1 until 11 step 2: 3
1 until 11 step 2: 5
1 until 11 step 2: 7
1 until 11 step 2: 9"
*/
val arr = IntArray(5) {it + 1}
for (i in arr) {
println("i in arr: $i")
}
/* Prints
"i in arr: 1
i in arr: 2
i in arr: 3
i in arr: 4
i in arr: 5"
*/
for ((index, i) in arr.withIndex()) {
println("$index's value: $i")
}
/* Prints
"0's value: 1
1's value: 2
2's value: 3
3's value: 4
4's value: 5"
*/
}
2. while
fun main() {
var num1 = 1
while (num1 <= 10) {
println("$num1")
num1++
}
/* Prints
"1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10"
*/
var num2 = 1
do {
println("$num2")
num2++
} while (num2 <= 10)
/* Prints
"1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10"
*/
}
3. continue & break
fun main() {
// Normal continue/break in the nested loop
for (i in 1..3) {
for (j in 1..5) {
if (j % 2 == 0) continue
println("$i, $j")
}
}
/* Prints
"1, 1
1, 3
1, 5
2, 1
2, 3
2, 5
3, 1
3, 3
3, 5"
*/
// Labeled continue/break in the nested loop
outer@ for (i in 1..3) {
for (j in 1..5) {
if (j % 2 == 0) continue@outer
println("$i, $j")
}
}
/* Prints
"1, 1
2, 1
3, 1"
*/
}
댓글